1. The main object in the frame
It’s not bad if your picture has a key object on which the viewer’s attention will be focused.

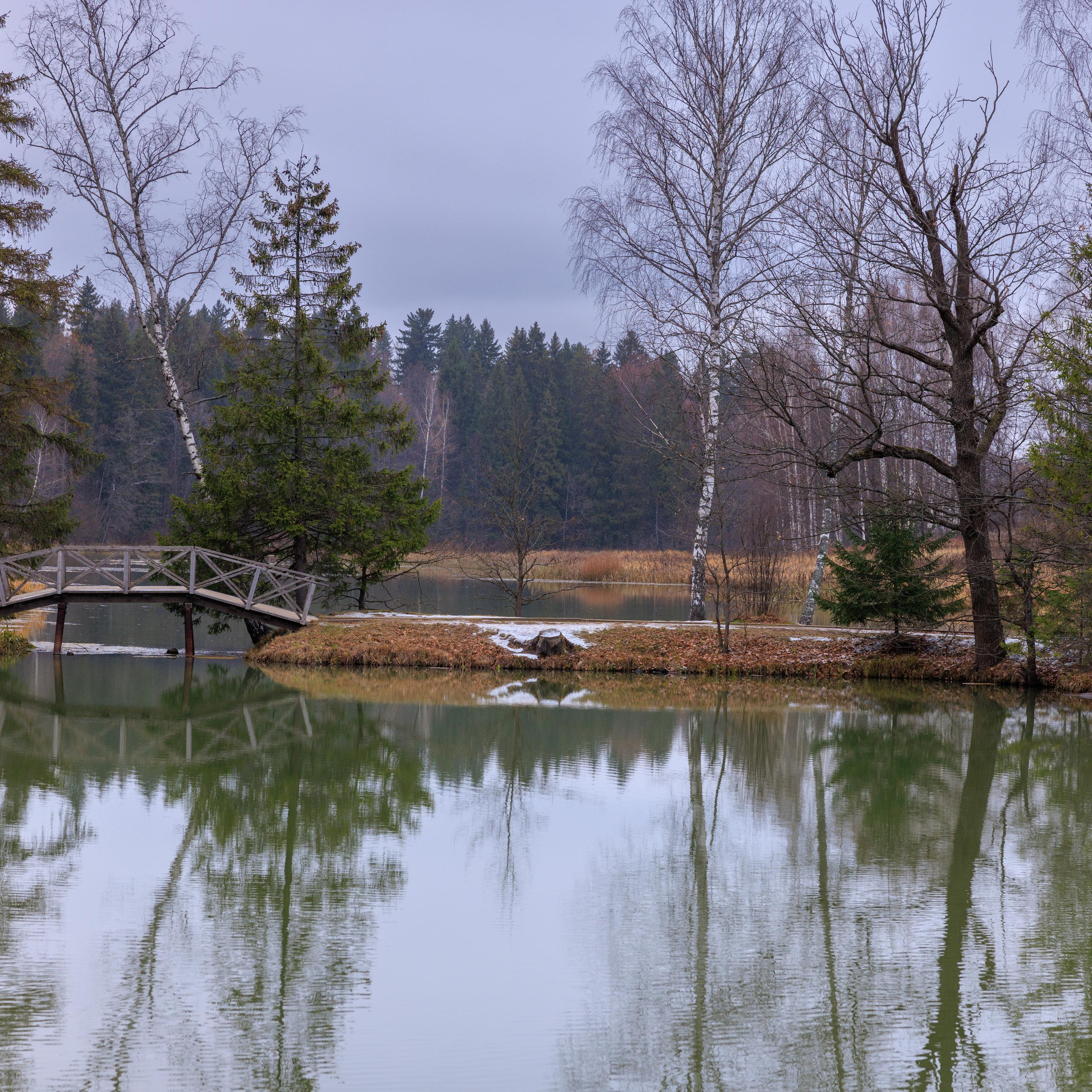
2. Diversity of the frame
It is desirable that your picture has a foreground, middle ground, and background. This trick creates 3D depth in the frame.
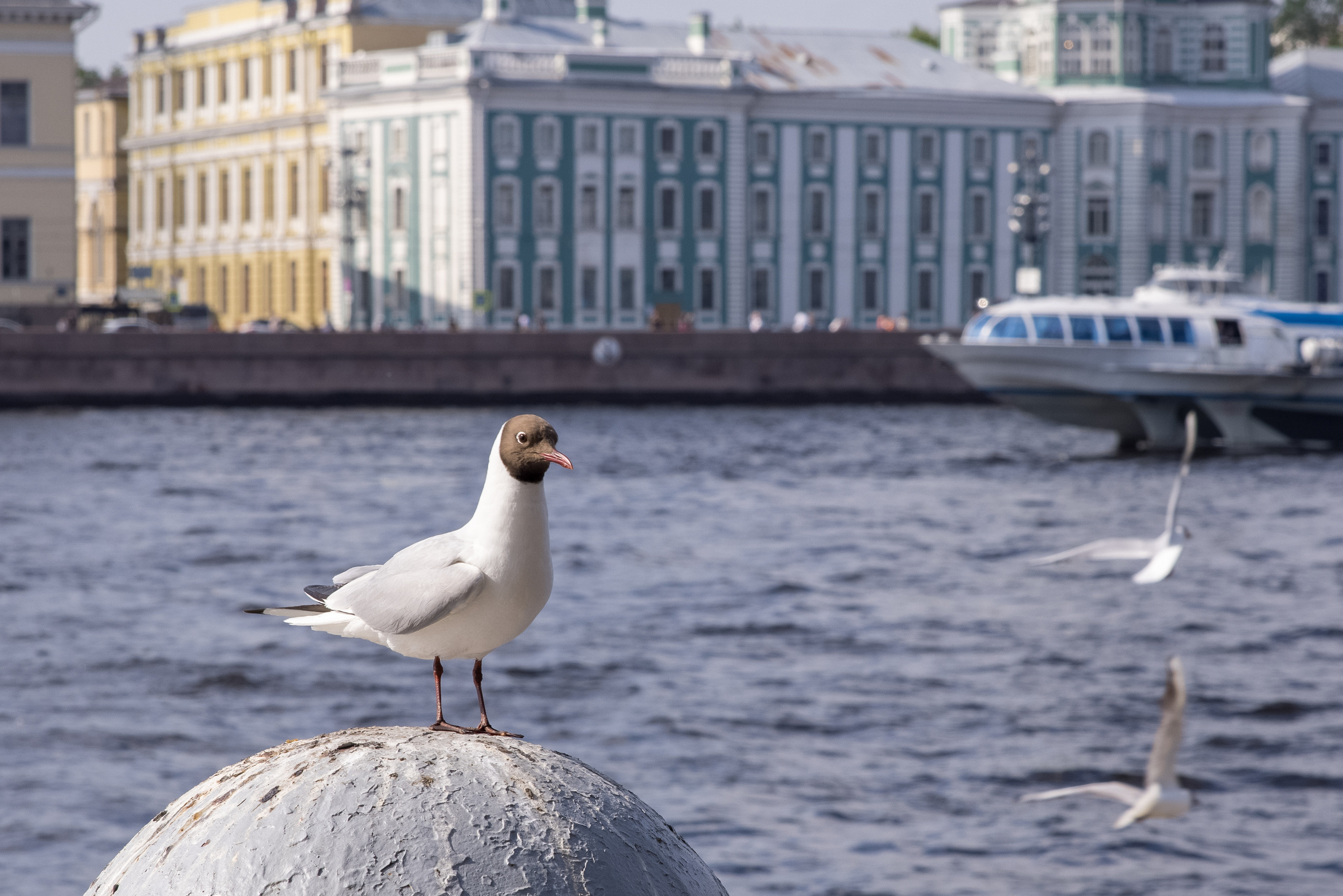
3. Defocus and depth of field
To add volume to the image, they also resort to such a technique as defocusing the space behind the main object. This artistic technique is called the bokeh effect.
This effect is achieved when shooting with a fast lens at the maximum aperture. At the same time, we focus on the desired object, and everything in front of it and behind it will be out of focus (blurred).

4. The rule of thirds
According to this rule, the key objects in the frame should be located at the intersection of lines that divide the image into 3 parts vertically and horizontally. For convenience, you can enable the display of these lines in your camera settings.

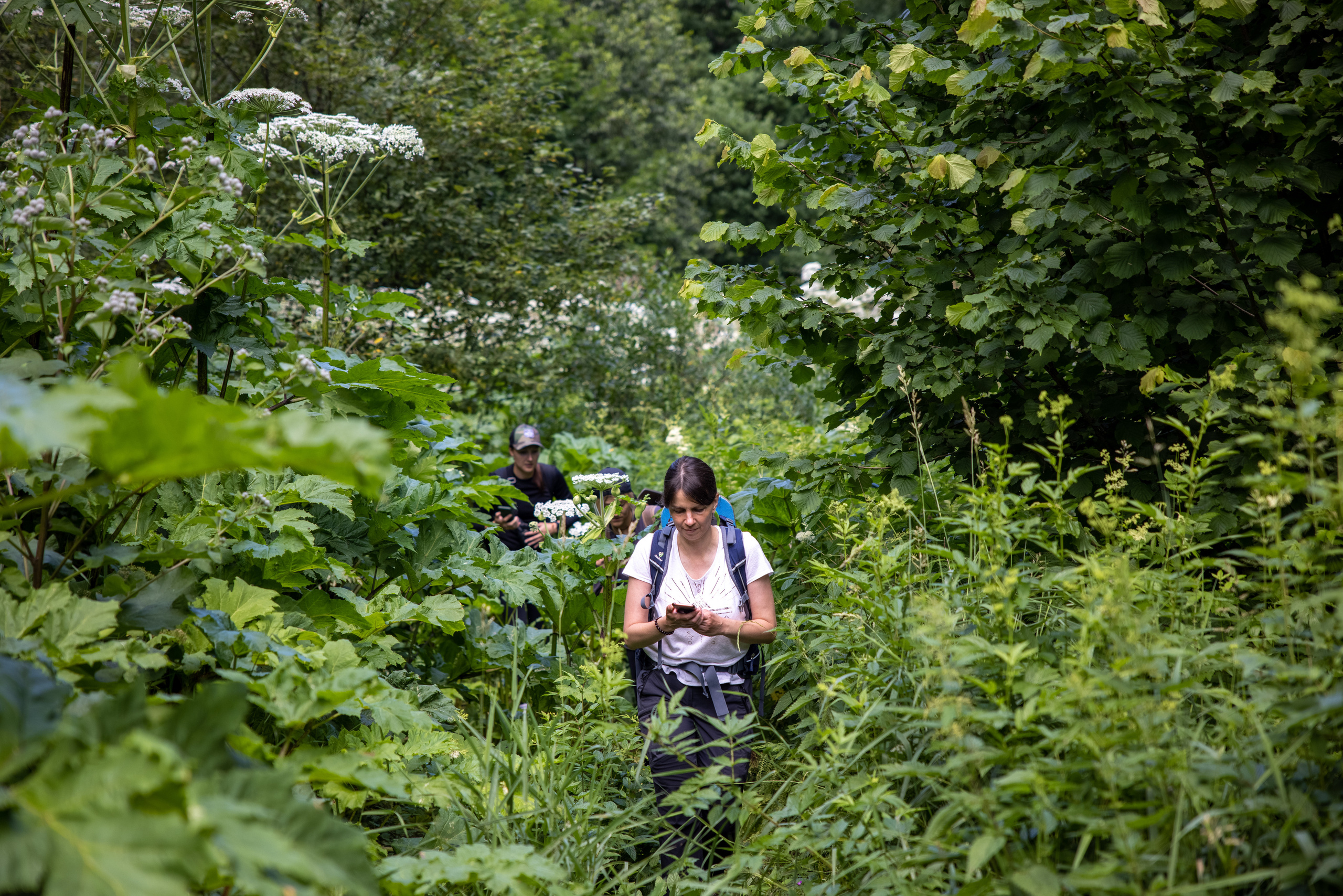
5. Framing
Framing (frame, framing) is like dressing your image in an artificial or natural frame.
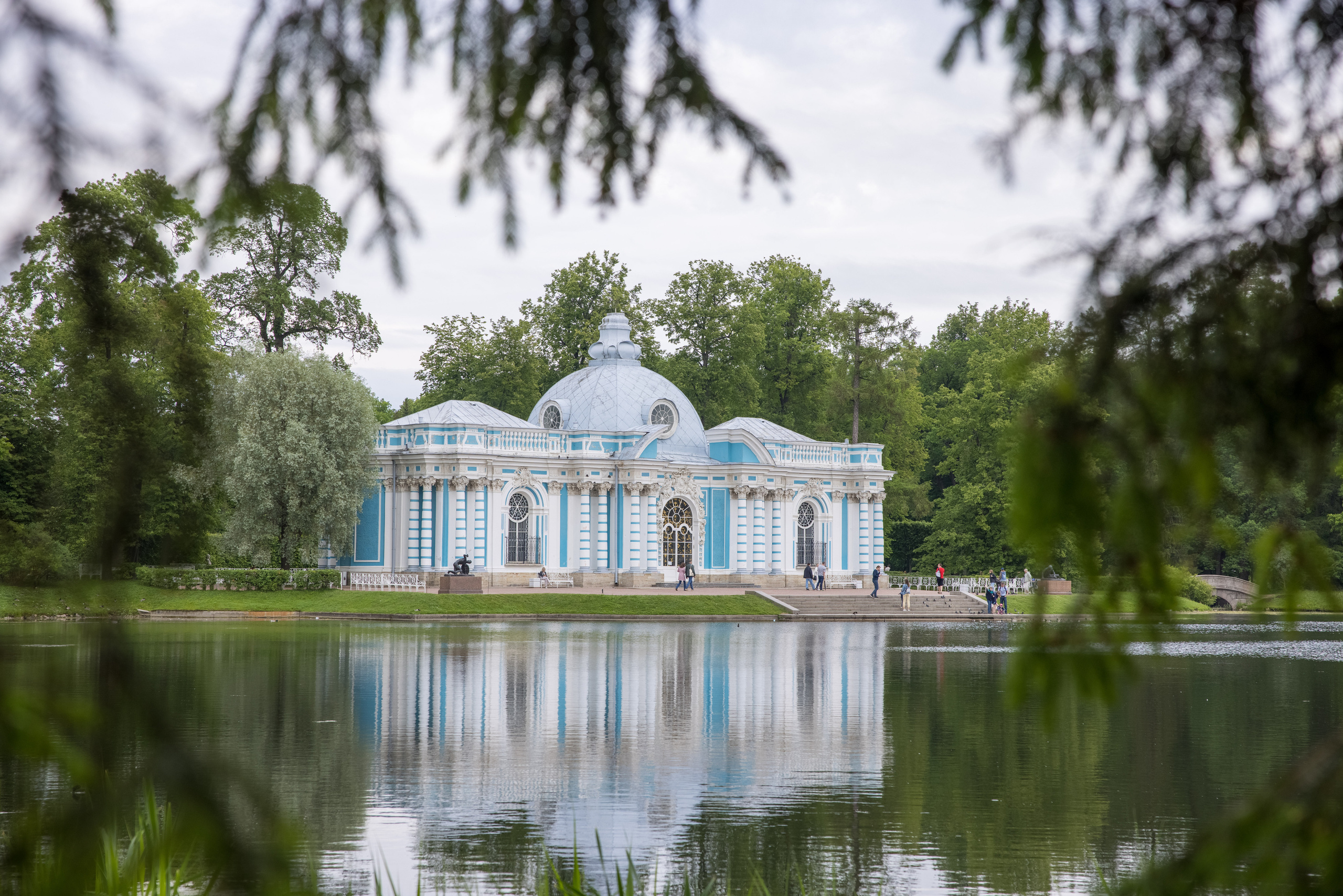

6. Rhythmic pattern
Pillars, steps, benches and other repeating objects that create a certain rhythm in the frame. Repeating drawings and patterns also form a beautiful rhythmic pattern.
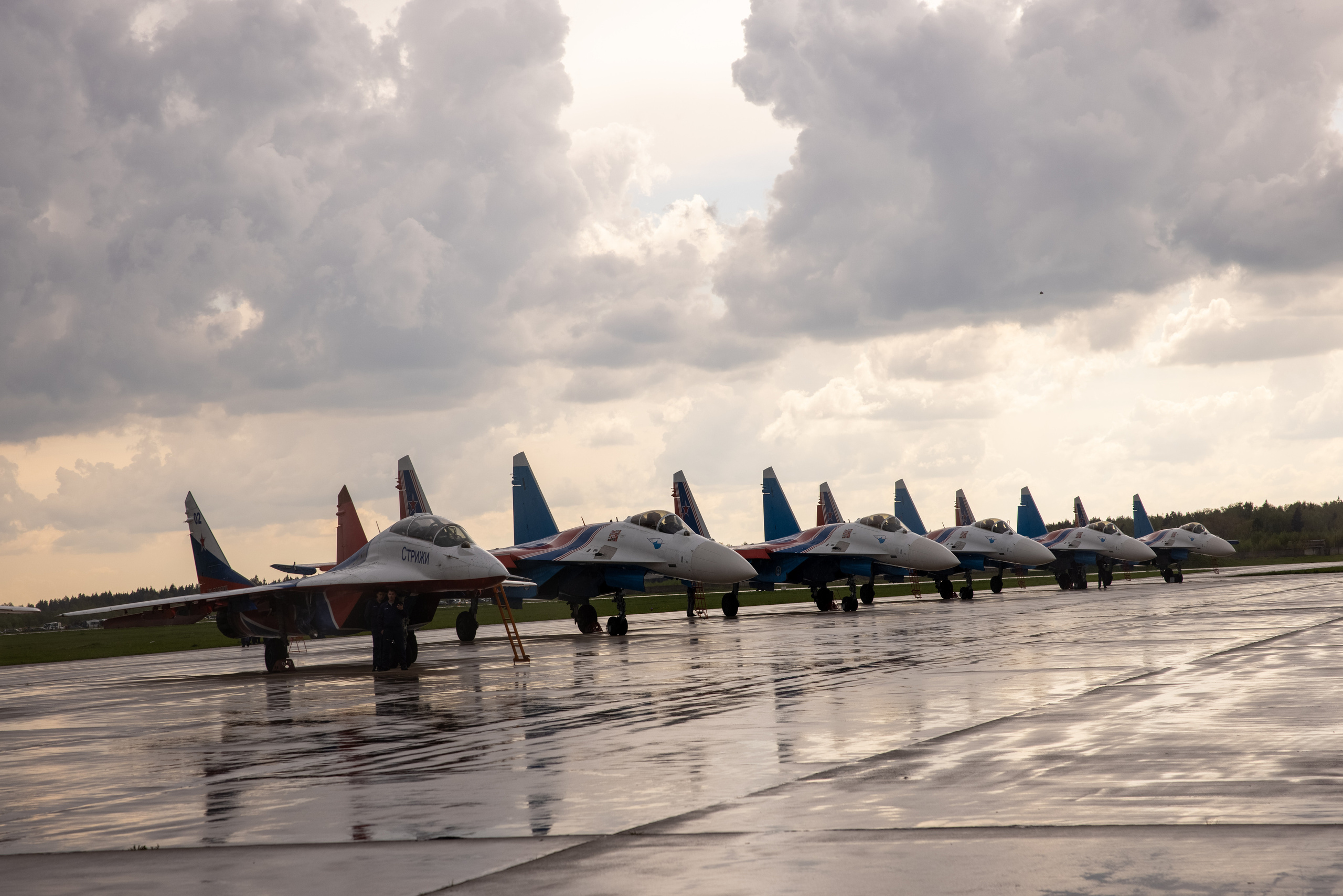

7. Symmetry
Proportionality of objects from the center line. The equidistance of these objects. In this case, the central line of symmetry can be either visible (for example, the horizon line) or not visible (an imaginary line).
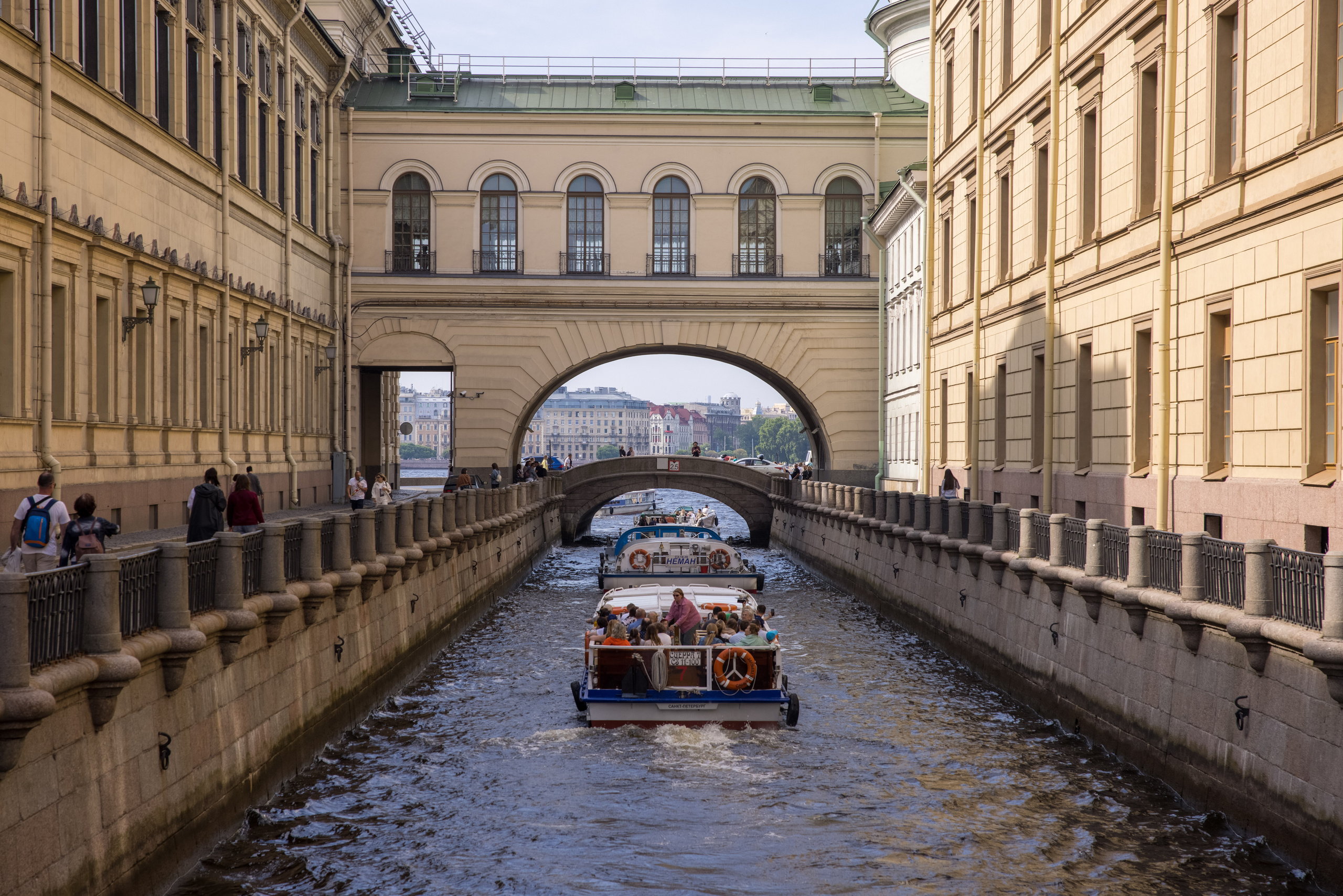

8. Diagonals
Diagonal lines and objects make the photo more dynamic, attract the viewer’s attention, guide their eyes through the entire frame.
There are “fast” (from the upper left to the lower right corner) and “slow” (from the lower left to the upper right corner) diagonals.
It is believed that the ascending diagonal (“slow”) causes appeasement, while the descending (“fast”) diagonal causes anxiety and anxiety.
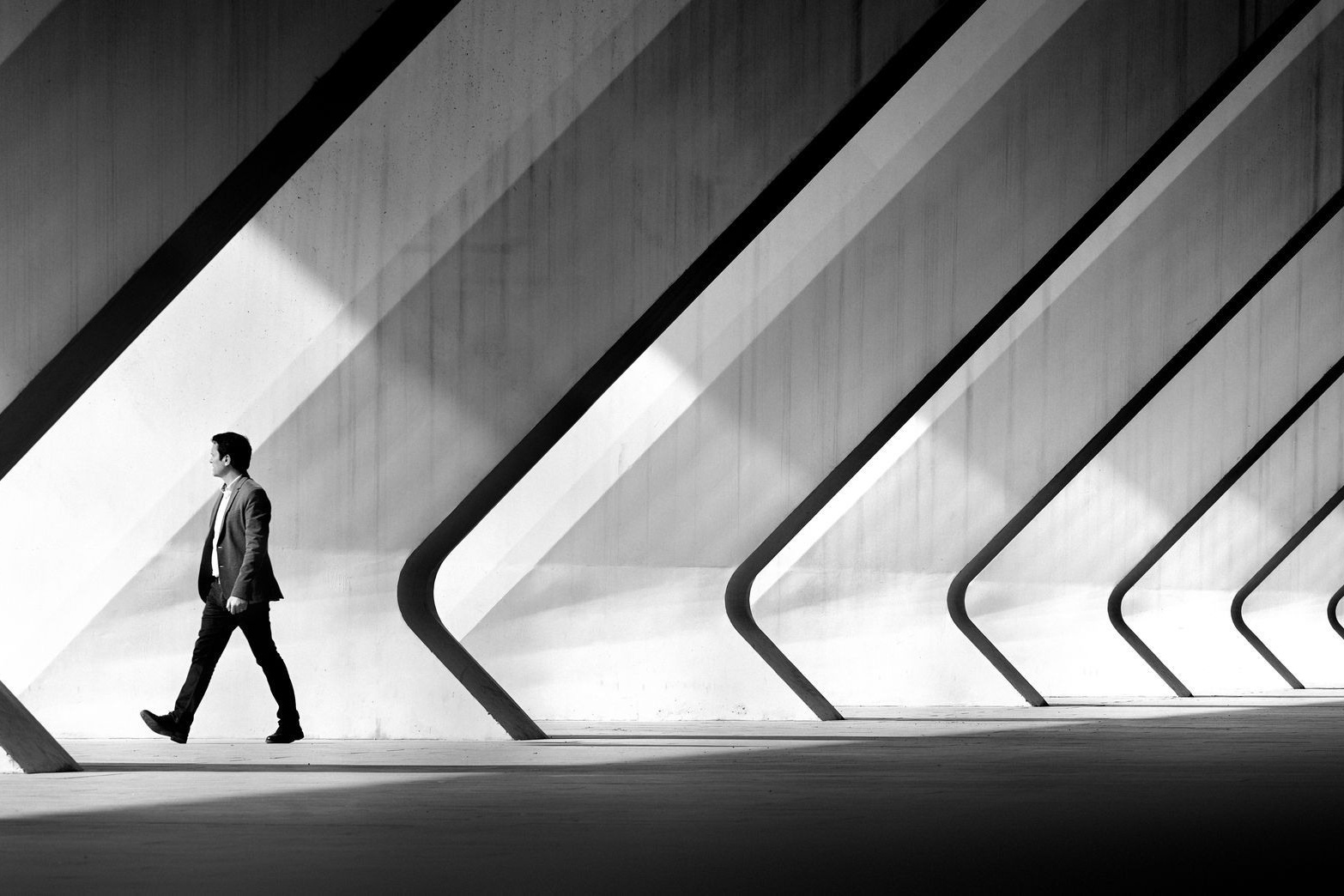

9. Guide lines.
Lines in the frame are used to direct the viewer’s eye. For example, the lines of a railroad track that join in the depth of the frame, or the lines of a long winding road leading the eye to the main object in the frame. They seem to lead the viewer’s eye across the frame to the object you need.
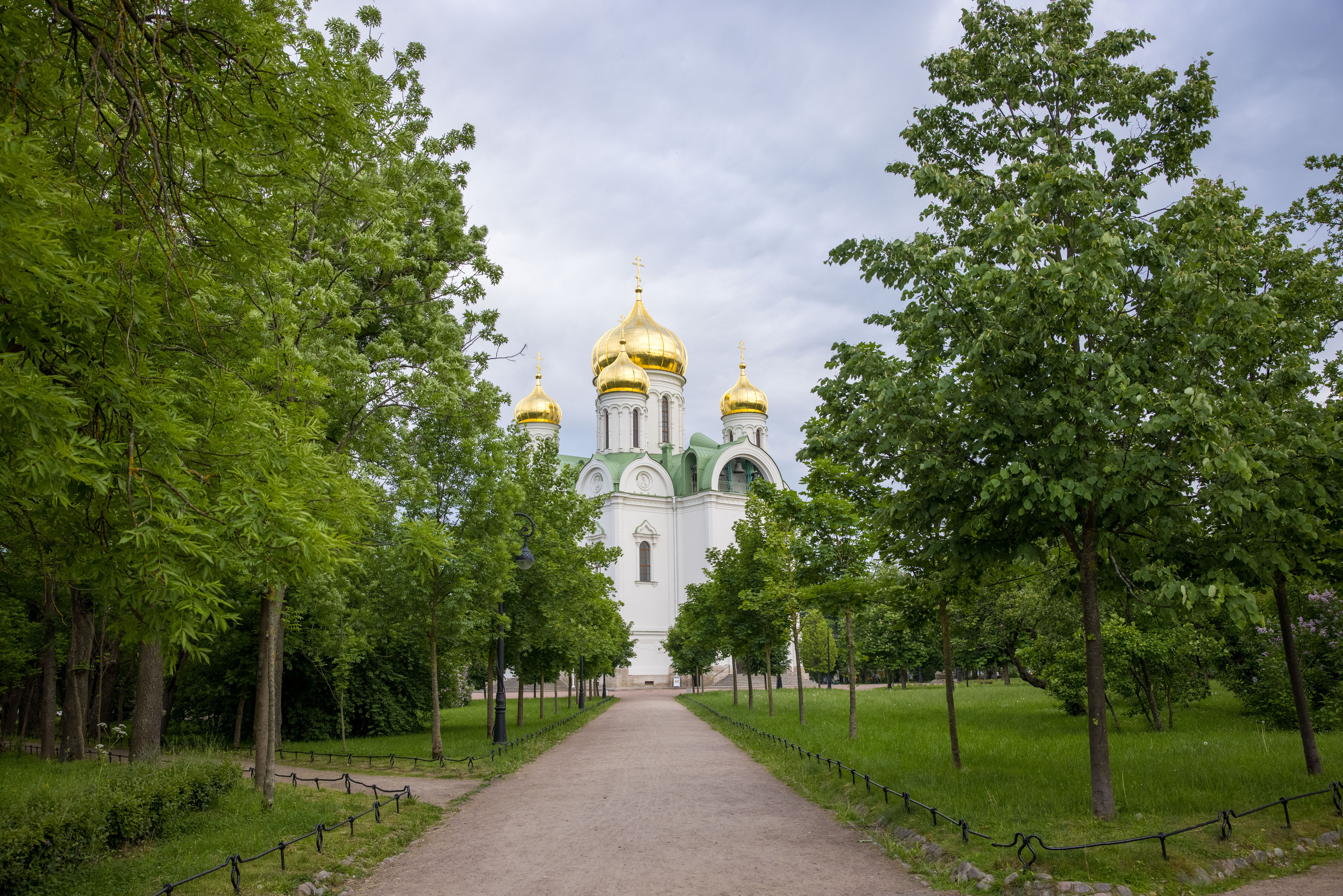

10. Negative space
Negative or negative space is the free area around the main image. Sky, wall, blurred background, etc. It shouldn’t be too much. It is necessary to observe a certain golden mean.
Focus on the fact that there can be about two more negative space in the picture than positive space.
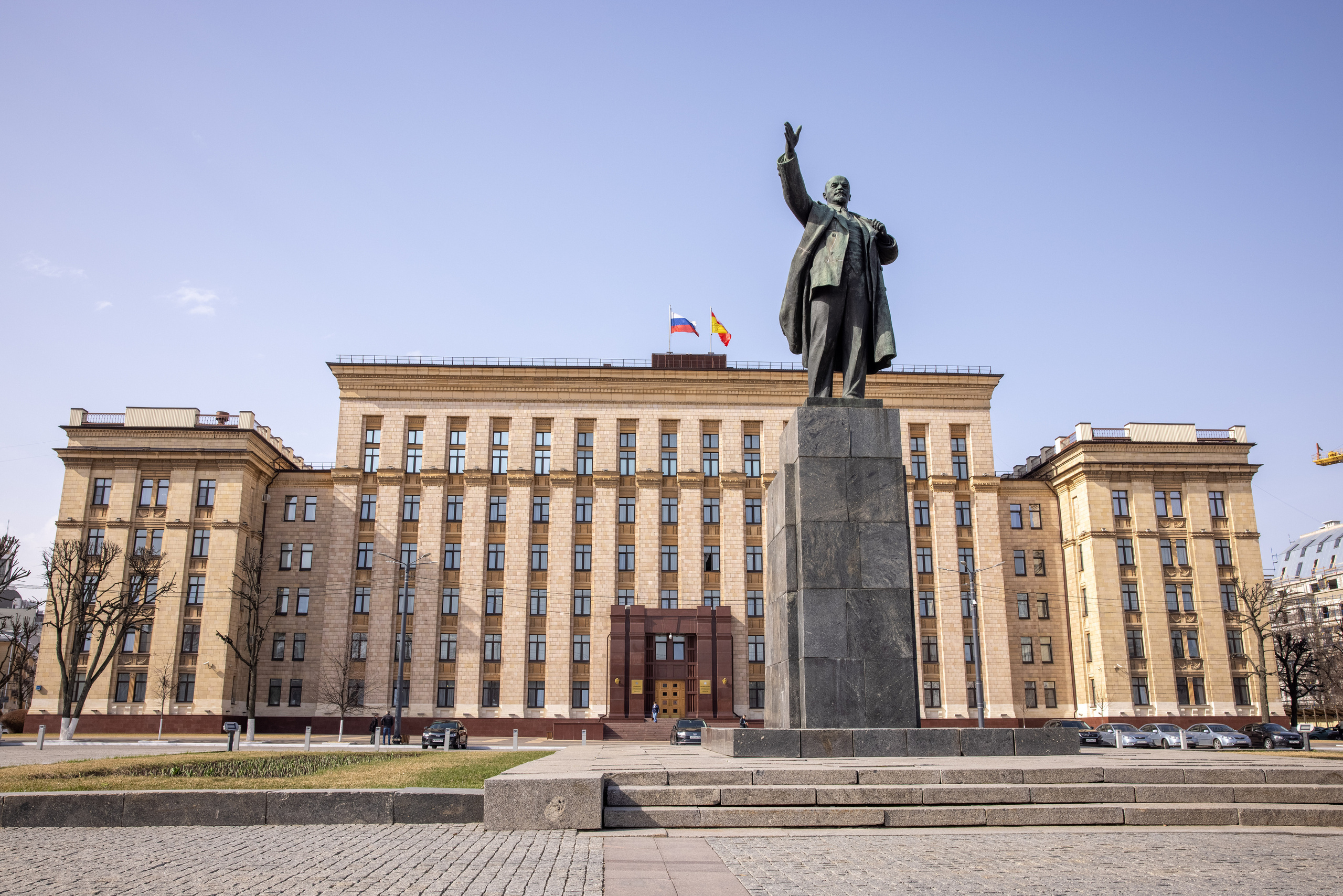

11. Filling the frame.
Maximum framing of the subject with almost no negative space.
It is used in shooting portraits, animals, architecture, macro photography.
It is important here to show details, texture, and place maximum emphasis on the subject.

Education

Настройки iPhone для съёмки качественного видео

Схемы света для студийного портрета
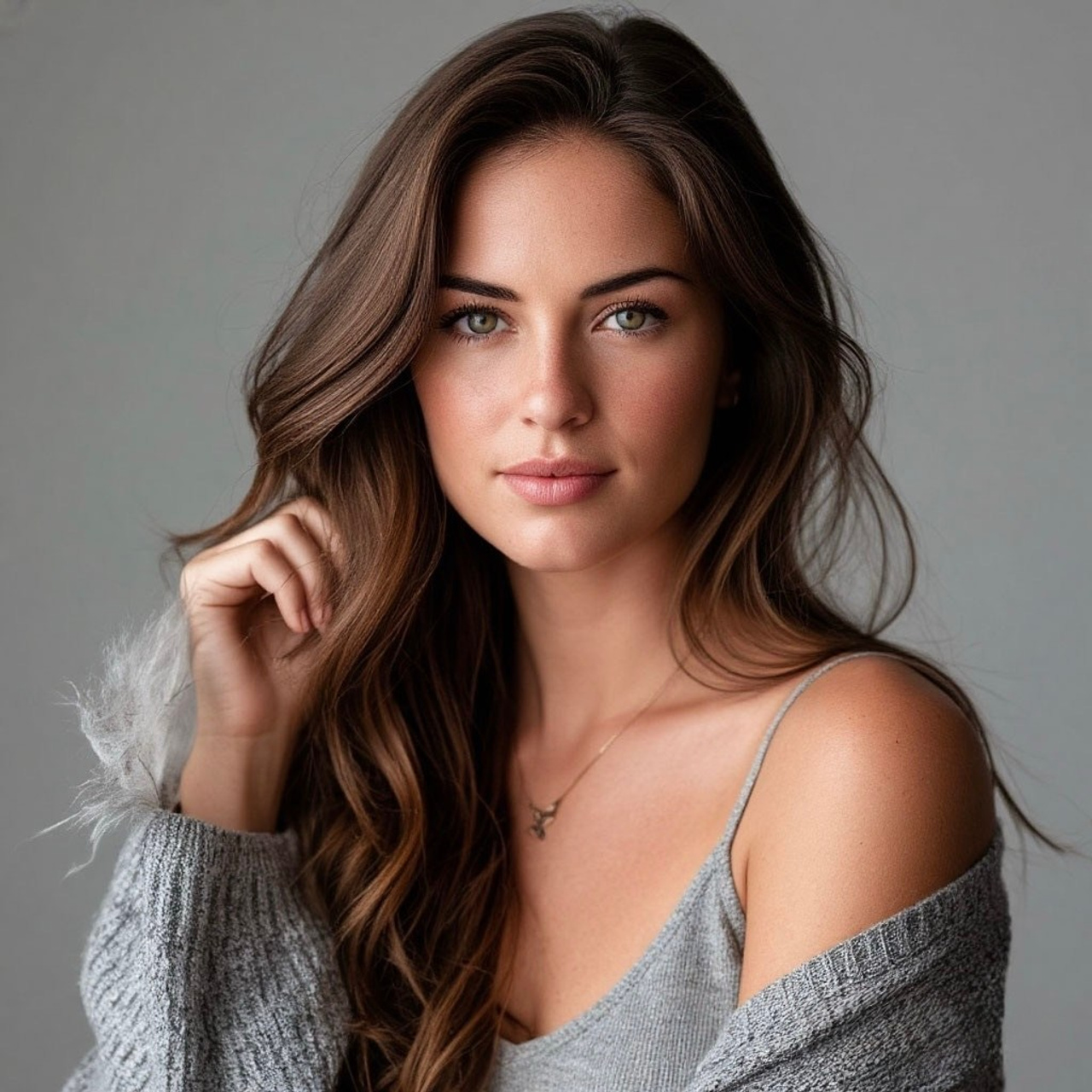

Основные женские позы для фотосессии: универсальный гид
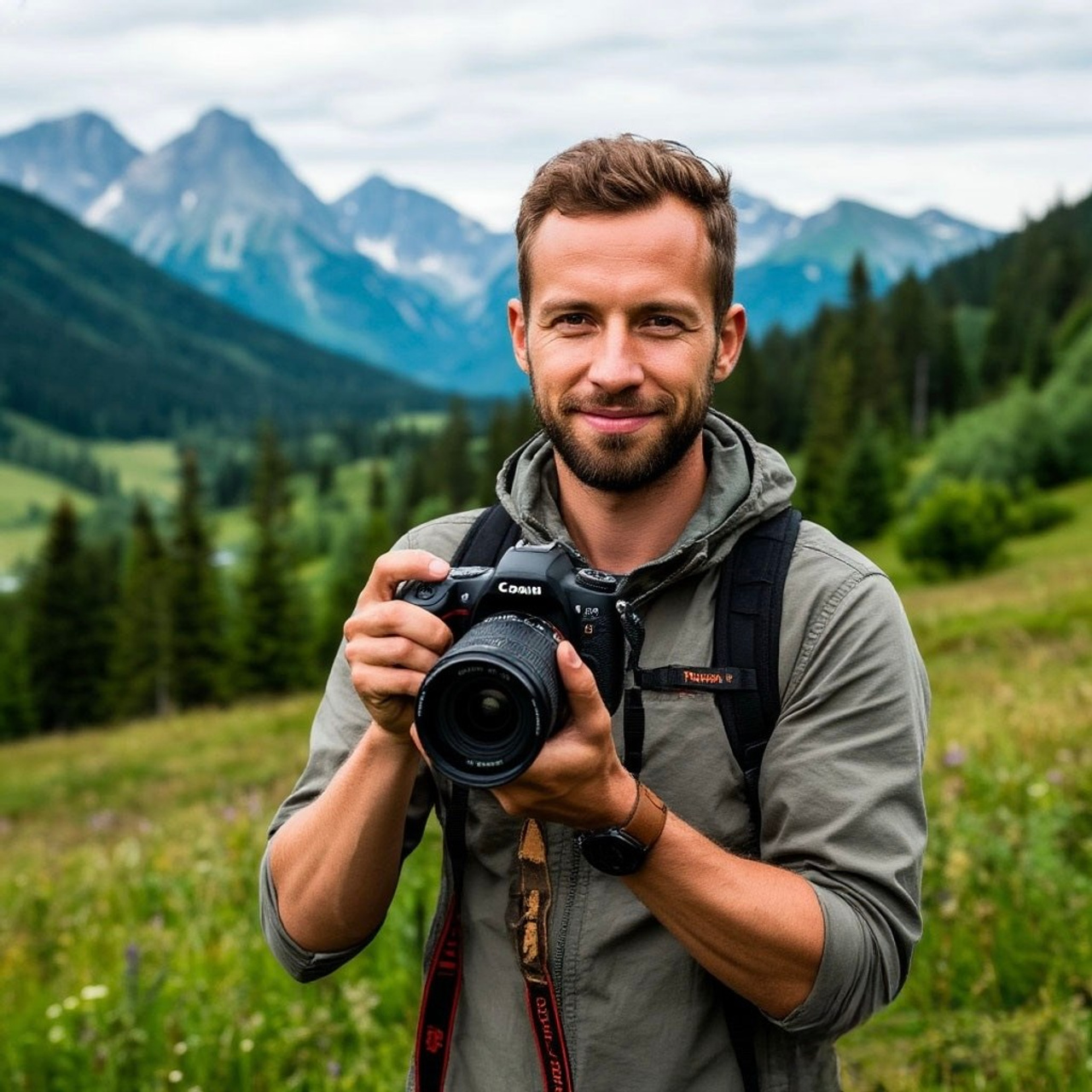

Секреты видео от Антона Птушкина: как снимает топовый тревел-блогер
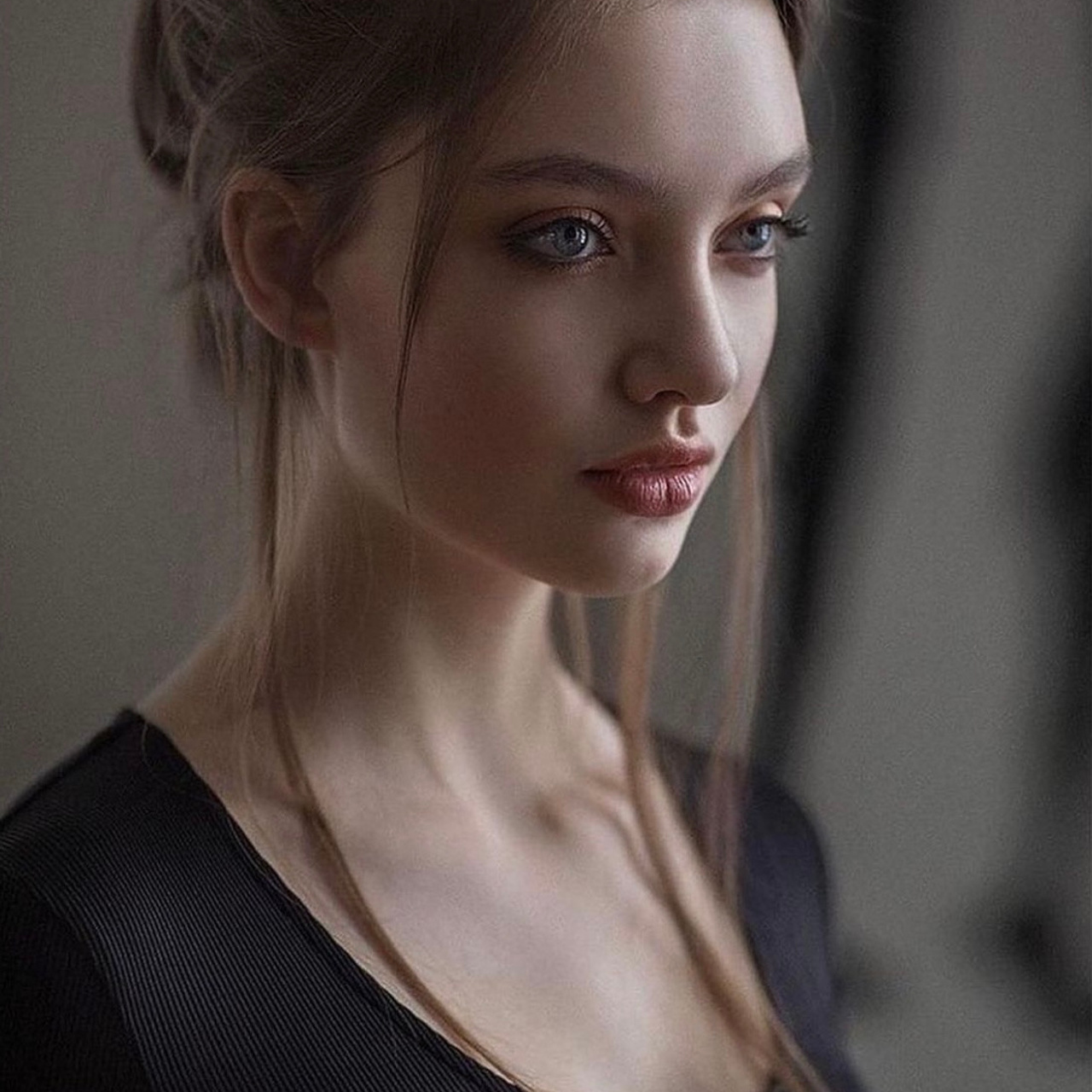

Shooting a portrait with natural light by Alexey Kazantsev

10 принципов видеомонтажа по Соколову

